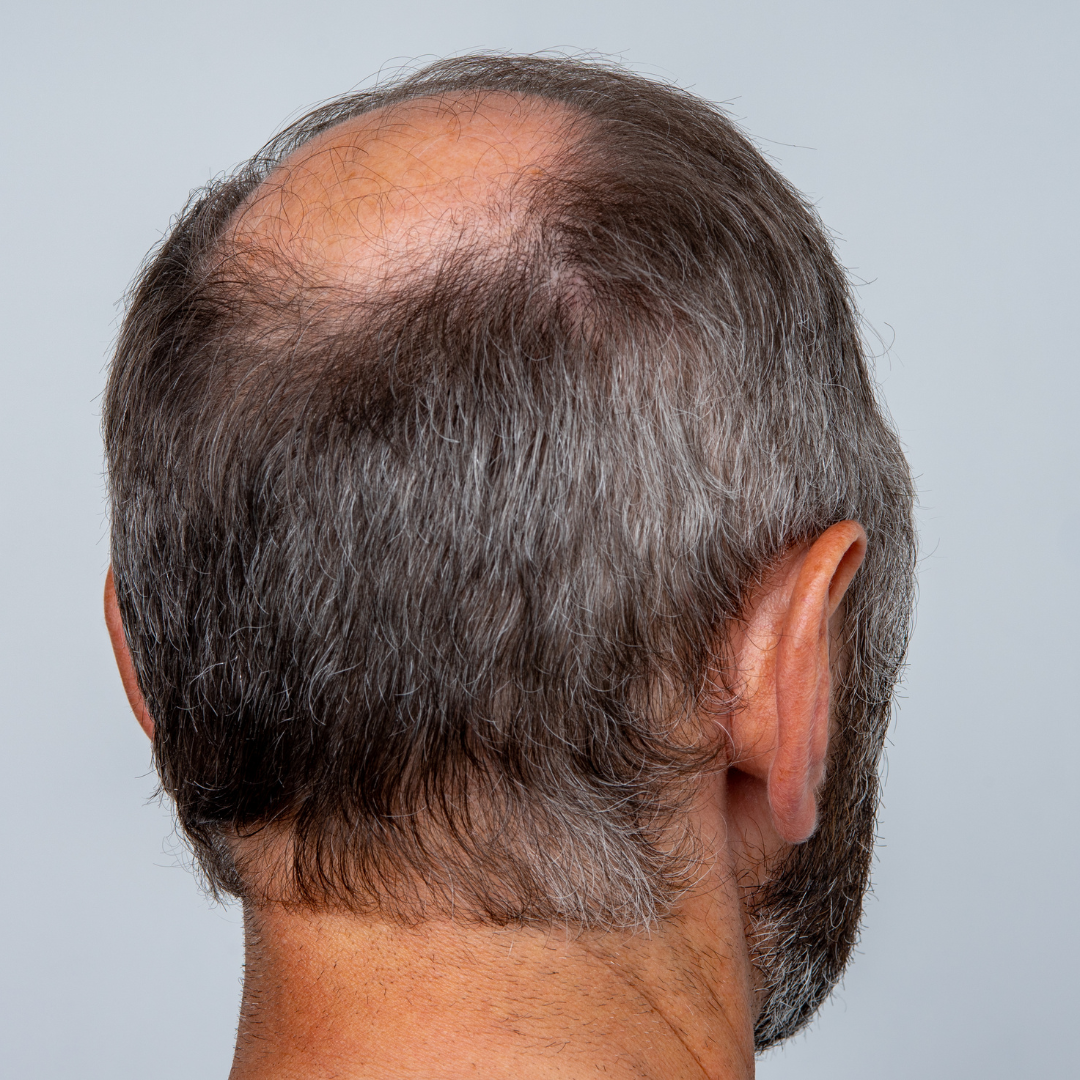
Male Hair Loss: Unveiling the Complex Interplay of Hormones, Genetics, and Emotion
Hair loss is a phenomenon that affects millions of men worldwide. While it's often considered a natural part of aging, the reality is far more complex. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on why men lose their hair, debunk common myths, and offer actionable solutions for those facing this issue.
The Science Behind Male Hair Loss
The Hair Growth Cycle
Understanding hair loss begins with understanding the hair growth cycle, which consists of three phases:
- Anagen: The growth phase lasting 2-6 years.
- Catagen: A transitional phase lasting 2-3 weeks.
- Telogen: The resting phase lasting 2-3 months, after which the hair falls out.
Types of Male Hair Loss
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Commonly known as male-pattern baldness, this is the most prevalent form of hair loss in men.
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disorder causing patchy hair loss.
- Telogen Effluvium: Temporary hair loss due to stress or trauma.
- Anagen Effluvium: Hair loss caused by chemotherapy or other medications.
The Role of DHT
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a hormone derived from testosterone. It plays a significant role in male-pattern baldness by shrinking hair follicles, making it difficult for healthy hair to survive.
Myths: The Stories We Tell Ourselves
The Age Fallacy
Contrary to popular belief, hair loss is not an exclusive domain of the aging male. Men in their late teens can find themselves confronting this issue, underscoring the role of genetics and hormones over age.
The Maternal Myth
While folklore often blames the mother's lineage for a man's receding hairline, science tells us that both parental genes are complicit. It's a genetic lottery where both sides of the family contribute tickets.
The External Variables
The Stress Connection
The body's stress response, a cascade of hormonal changes, can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to temporary but alarming hair loss. This form of loss, known as Telogen Effluvium, is reversible but psychologically distressing.
The Nutritional Equation
A well-balanced diet is not just fuel for the body; it's nourishment for the hair. Deficiencies in essential nutrients like iron and protein can lead to hair thinning, adding another layer to the complex etiology of hair loss.
The Diagnostic Lens
From scalp biopsies to blood tests and advanced trichoscopy, diagnostic methods have evolved to offer a nuanced understanding of hair loss. These tools not only identify the type of hair loss but also uncover underlying systemic issues, offering a holistic view of the problem.
Contributing Factors
Stress
High stress levels can lead to temporary hair loss due to the body's hormonal response.
Diet and Nutrition
Lack of essential nutrients like iron, protein, and vitamins can contribute to hair thinning.
Medications and Treatments
Certain medications, including those for blood pressure and chemotherapy, can cause hair loss.
Lifestyle Choices
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to hair loss.
Diagnostic Methods
Scalp Biopsy
A small section of the scalp is removed to examine the hair follicles.
Blood Tests
These can identify any underlying issues related to hormones or nutrient deficiencies.
Trichoscopy
A digital imaging technique used to analyze the scalp and hair.
Treatment Options
Minoxidil
An over-the-counter topical treatment that can slow hair loss and promote new growth.
Finasteride
A prescription medication that inhibits the conversion of testosterone to DHT.
Hair Transplant
A surgical procedure where hair follicles are moved from one part of the body to the balding area.
Laser Therapy
Low-level lasers can stimulate hair follicles and improve hair density.
Preventive Measures
Balanced Diet
A diet rich in essential nutrients can support healthy hair growth.
Stress Management
Practices like meditation and exercise can help manage stress levels, reducing the risk of hair loss.
Regular Check-ups
Frequent medical check-ups can help catch any underlying issues before they lead to hair loss.
The Psychological Impact
Hair loss can have a profound impact on a man's self-esteem and mental well-being. Support from loved ones and professional counseling can help men cope with the emotional aspects of hair loss.
Conclusion
Male hair loss is a complex issue influenced by various factors, including genetics, hormones, and lifestyle choices. While some myths persist, understanding the science behind hair loss can empower men to take proactive steps in managing this condition. With a range of treatment options available, there's hope for those looking to restore their locks and confidence.










